If you’re like most people, you probably don’t give much thought to the food you eat beyond whether or not it tastes good. However, what you eat can have a big impact on your health in the short and long run. Here are some common food-related health conditions that you should be aware of:
Obesity
Obesity is a food-related health condition that has become more prevalent in recent years. It is characterized by an excessive amount of body fat. It can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems. While obesity can be caused by several factors, such as genetic predisposition or hormonal imbalance, the most common cause is overeating.
Consuming more calories than the body can burn leads to weight gain, leading to obesity. The good news is that obesity is reversible. By making healthier food choices and increasing physical activity, it is possible to lose weight and improve overall health.
Heart Disease
You might not realize it, but what you eat can directly impact your risk of developing heart disease. In fact, poor diet is one of the leading causes of heart disease. Eating foods high in saturated fat and cholesterol can contribute to plaque build-up in your arteries, leading to heart attack or stroke. Foods high in sugar can also increase your risk of heart disease, as they can cause inflammation and contribute to weight gain.
On the other hand, eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to protect your heart. So if you’re looking to improve your heart health, be sure to start with your diet.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a food-related health condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. The condition can be caused by several factors, including insulin resistance and poor diet. Foods high in sugar, fat, and calories can all contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, eating large amounts of processed foods or sugary drinks can increase your risk for the condition. Making healthy choices regarding your diet is one of the best ways to prevent type 2 diabetes. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to keep your blood sugar levels in check. In addition, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight are important factors in preventing type 2 diabetes.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a food-related health condition caused by a lack of calcium in your diet. It can also be caused by a lack of vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium. Osteoporosis can also be caused by a lack of exercise, leading to bone density loss. Finally, osteoporosis can be caused by a family history of the condition.
If you are at risk for osteoporosis, there are some things you can do to help prevent it. First, make sure you are getting enough calcium in your diet. You can get calcium from milk, cheese, yogurt, and leafy green vegetables. You should also ensure you are getting enough vitamin D. You can get vitamin D from sunlight, fish, and fortified milk. Finally, make sure you are getting enough exercise. Exercise helps to keep your bones strong and healthy. If you have osteoporosis, there are treatments available that can help to improve your quality of life. These treatments include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, or GERD, is a food-related health condition that affects the esophagus. The esophagus is what carries food from the mouth to the stomach. When you have GERD, the acids in your stomach and other liquids move back from your stomach into your esophagus. This can cause heartburn, chest pain, and other symptoms.
GERD is more common in people who are overweight or obese, and it can be made worse by certain foods and drinks, such as spicy food, citrus fruit, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol. If you have GERD, your doctor may recommend changing your diet, such as eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and eating more slowly. In some cases, medication may also be necessary to control symptoms.
Food Allergies
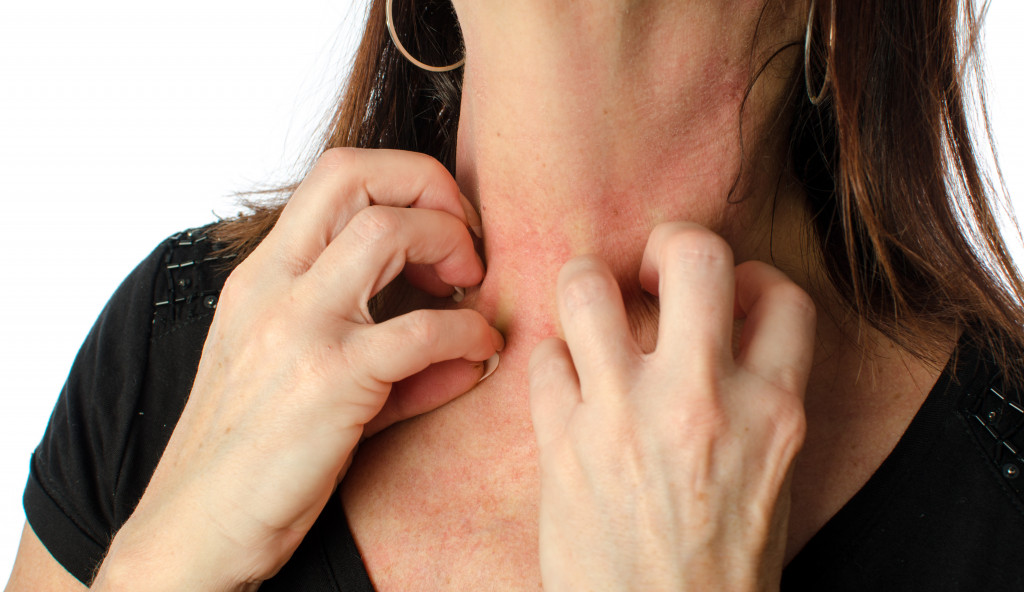
Food allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly sees a certain food as harmful and reacts to it. Symptoms of a food allergy can range from mild, such as itching or hives, to severe, such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. Common food allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, dairy, wheat, eggs, fish, shellfish, and soy.
There is no cure for food allergies, and the only way to prevent a reaction is to completely avoid the allergen. It’s important to read labels carefully and always ask about ingredients when eating at restaurants. In severe cases, carrying an epinephrine injector may also be necessary in case of accidental exposure to an allergen.
If you’re unsure about a food allergy, go to an allergy test clinic. This can help you find out if you have any food allergies and develop a plan to avoid them. The health professionals in the clinic can also provide support and guidance for managing food allergies.
These are just a few of the many potential health problems that can be caused by what you eat. So next time you’re reaching for something to snack on, remember to think about how it might affect your health—both in the short and long run!

