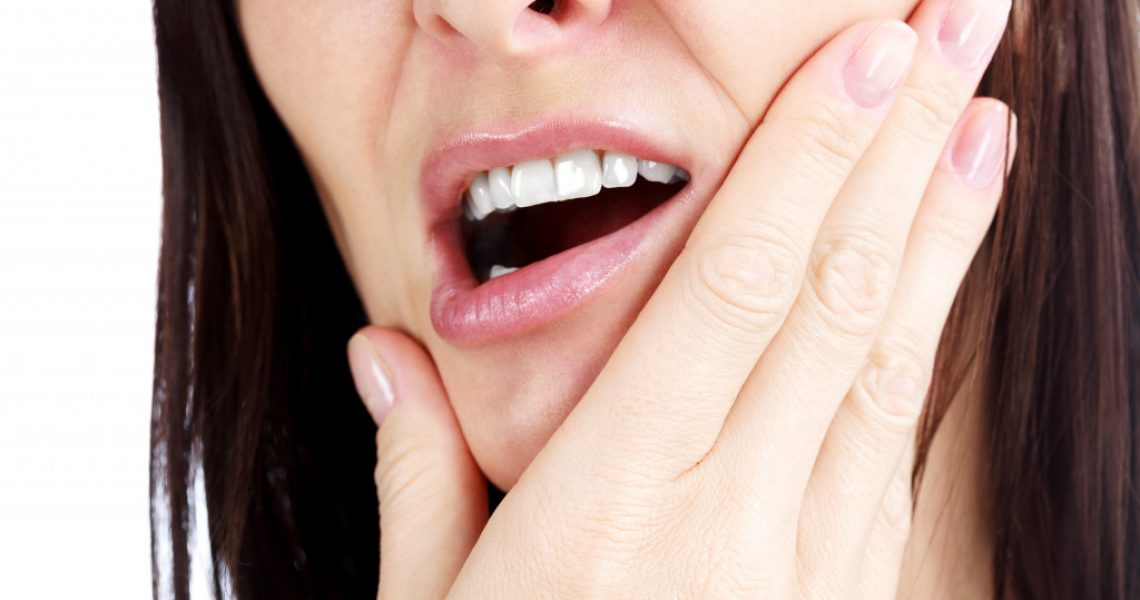
• Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection of the gums and bones supporting teeth, which can cause tooth loss and other serious health issues if left untreated.
• Risk factors for periodontal disease include smoking/tobacco use, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, age, and heredity.
• The best way to reduce your risk of periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene habits and visit a dental clinic for regular checkups and professional cleanings.
• Additionally, quitting smoking or using other forms of tobacco can also help reduce your risk.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a chronic bacterial infection affecting the gums and bones supporting teeth. It is one of the most common dental diseases, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other more serious health issues. Here’s what you need to know about periodontal disease.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is an inflammatory condition caused by bacteria in plaque buildup around your gums. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on the surface of your teeth. When plaque isn’t removed with proper brushing and flossing techniques, it hardens into tartar (calculus). This creates a breeding ground for bacteria which can cause inflammation and infection in the gums. Periodontal disease can spread below the gum line when left untreated, leading to tooth loss and other serious health concerns.
Risk Factors
There are various reasons why people might develop periodontal disease. Here are some of them:
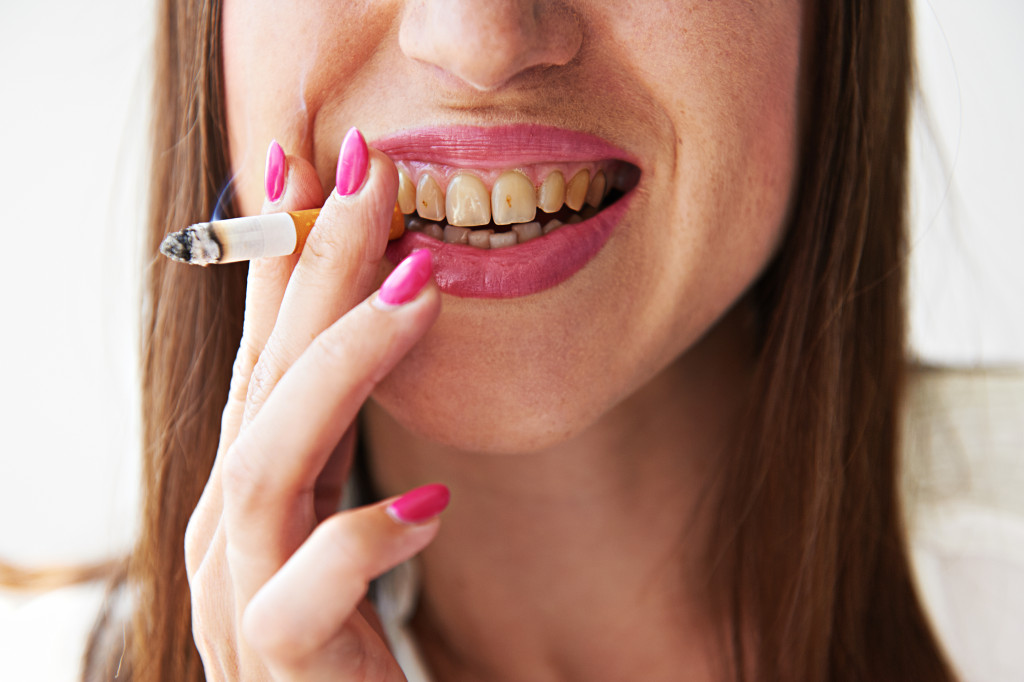

Smoking or Tobacco Use
Using tobacco products such as cigarettes and chewing tobacco has been linked to an increased risk of developing periodontal disease. Tobacco use increases your body’s production of bacteria-fighting compounds that can damage your gums and teeth over time. Quitting smoking or using other forms of tobacco can reduce your risk for periodontal disease.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing periodontal disease. Brushing and flossing regularly will help remove plaque and tartar buildup on your teeth, which can lead to gum inflammation and infection if left unchecked. It is also important to visit your dentist twice a year for professional cleanings so any plaque buildup you may have missed can be removed before it causes further damage to your gums or teeth.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes in women due to pregnancy, menopause, or certain medications can increase their risk of developing periodontal disease. Hormonal changes cause fluctuations in estrogen levels, making the gums more sensitive to bacteria-causing plaque, leading to inflammation and infection in the gums if not treated properly.
Age & Heredity
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for developing the periodontal disease since it increases the chances of poor oral hygiene habits forming over time and weakening the body’s defenses against infection. Additionally, heredity plays a role; some people are genetically predisposed to weaker immune systems, making them more susceptible to bacterial infections such as those that lead to periodontal disease.
Preventing Periodontal Disease
A periodontal disease is an advanced form of gum disease that can result in tooth loss and other serious health issues if left untreated. Fortunately, there are many things you can do to prevent periodontal disease or manage it if it has already developed.
Visit a Dental Clinic
One of the best ways to reduce your risk of periodontal disease is to visit a dental clinic for regular checkups and professional cleanings. You visit many dental clinics, like MetroDental clinic, for a periodontal check-up. During these visits, your dentist or hygienist can remove plaque and tartar buildup that you may have missed with brushing and flossing. They can also look out for signs of gum disease and recommend proper treatments if necessary.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Another way to reduce your risk of periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing regularly, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and avoiding sugary treats.
Quit Smoking
One of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of periodontal disease is to quit smoking or using other forms of tobacco. Tobacco use increases the number of bacteria-fighting compounds in your body, which can damage your gums and teeth over time if left unchecked. Quitting smoking will help reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease and other serious health conditions.
Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection affecting the gums and bones supporting teeth. Even though it’s one of the most common dental diseases, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk or manage it if it has already developed. Once you do, you can prevent gum disease and its effects on oral health.

